اعتذر عن عدم الترجمة تقبلوا اعتذاري Tu-95RTs Bear D Reconnaissance and Targeting Ту-95РЦ Разведчик-Целеуказатель  The Tu-95RTs Bear D Reconnaissance and Targeting platform was a specialised variant of the Tu-95 Bear A which emerged during the mid 1960s. It was developed to provide the airborne reconnaissance and targeting component of the МЦРС-1 «Успех» (MTsRS-1 Uspekh or Success) system, built around a massive ventral X-band acquisition and guidance radar, which was used to target ASCMs launched by Soviet warships and submarines. These were initially the P-5/P-6/P-35 Shaddock/Sepal, and later the P-500/P-1000 Sandbox series. The Bear D remained in service until the early 1990s, when it was replaced with satellite technology. The Bear D was progressively upgraded through its service life, and as newer ASCMs were deployed, its role shifted increasing to target acquisition and cueing SSG/SSGN and CG missile delivery systems rather than direct missile guidance.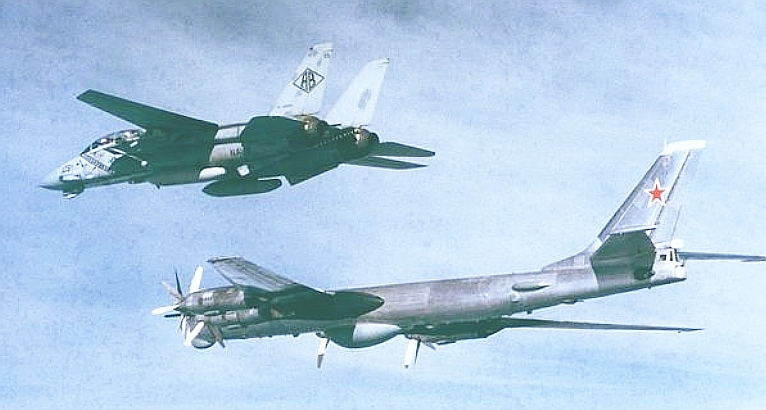    |
|||
Tu-95K/KD/KM Bear B/C Maritime Strike Ту-95КД/КМ Бомбардировщик-ракетоносец  The Tu-95K/KD/KM Bear C strike aircraft was the first cruise missile carrier variant of the Bear, developed during the late 1950s to attack strategic targets and opposing naval forces. Its primary weapon was the large Mach 1.8-2.0 11 tonne Al-7F turbojet powered Raduga Kh-20 / AS-3 Kangaroo, armed with a 2 tonne weight 800 kilotonne (Kh-20 baseline) or 3 Megatonne (Kh-20M) yield nuclear warhead. The inertial / command link guided Kh-20 was cumbersome and disappeared from service use by the 1970s, progressively replaced with the liquid rocket powered Raduga Kh-22 Burya / AS-4 Kitchen. The most visible design change is the distinctive nose radome for the large A-336Z YaD / Crown Drum attack radar used for targeting the Kh-20 missile.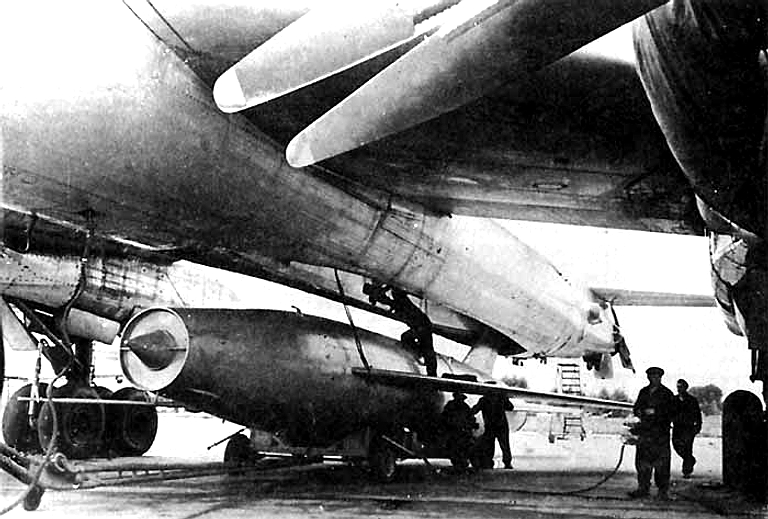 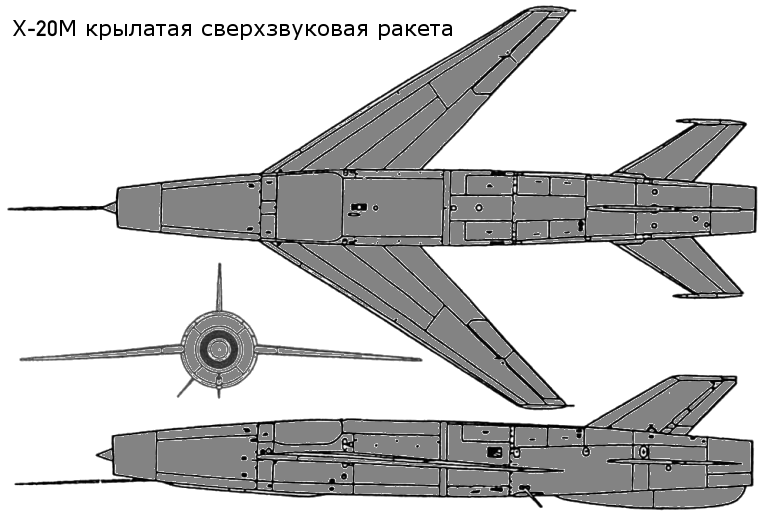  Above: loading the 10 tonne launch weight Kh-20 / AS-3 Kangaroo into the Bear C semi-conformal weapon bay; below: Bear C launching the Kh-20 / AS-3 Kangaroo cruise missile.   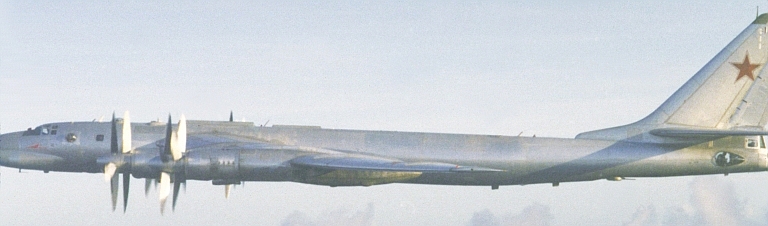  |
|||
Tu-95K-22 Bear G Maritime Strike Ту-95К-22 Бомбардировщик-ракетоносец 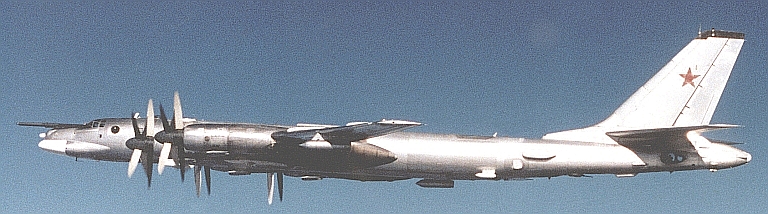 The Tu-95K-22 Bear G was a progressive block upgrade of the Bear B/C fleet, in which the Kh-20 weapon system was replaced by the Raduga Kh-22 / AS-4 Kitchen weapon system. The YaD attack radar was replaced with the Backfire's Leninetz PNA-B Down Beat, and three BD-45K/F adaptors were installed to carry the Kh-22. The Kh-20 semiconformal weapon bay was altered to fit the BD-45F, and wing root pylons were introduced to mount a pair of BD-45K, for a total warload of up three rounds. The distinctive recognition features of the Bear G are the unique tailcone fairing, mid fuselage and thimble nose radomes, which house emitters for the SPS-151/152/153 Lyutik self protection jammers, common to the MiG-25RBV and MiG-25BM Foxbat, and some Tu-16P Badger subtypes; and the aft fuselage blister radomes for the Kurs N/NM RHAW used to target anti-radiation variants of the Kh-22.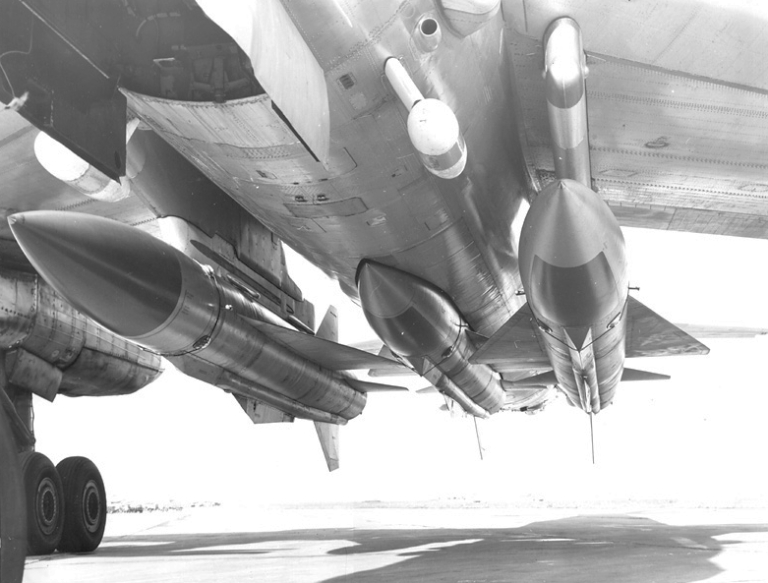      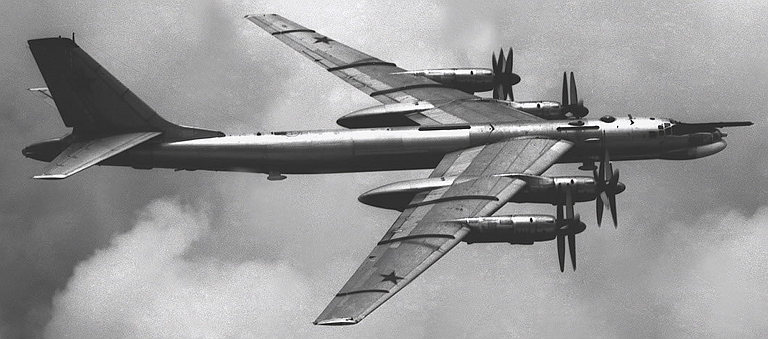   |
|||
Tu-95MR Bear E Maritime Reconnaissance Ту-95МР Разведчик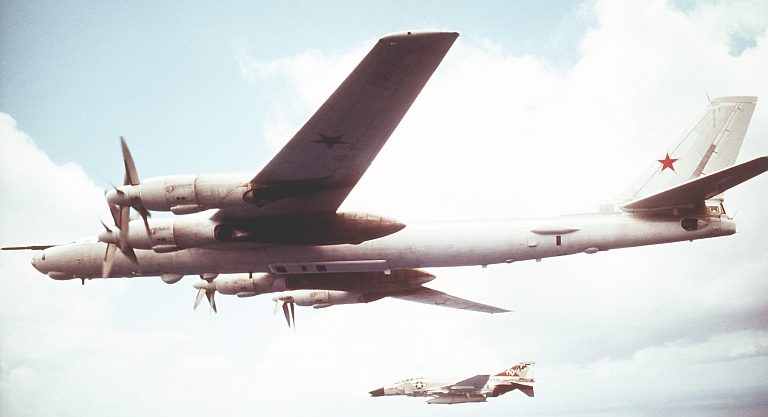  The Tu-95MR Bear E was a reconnaissance and intelligence gathering variant introduced during the early 1960s. They were progressively converted to trainers by the 1980s, as the newer Tu-142 and Tu-95RTs subsumed their role.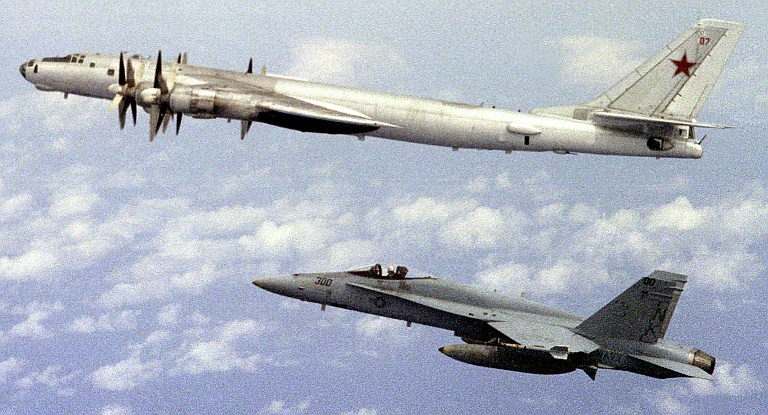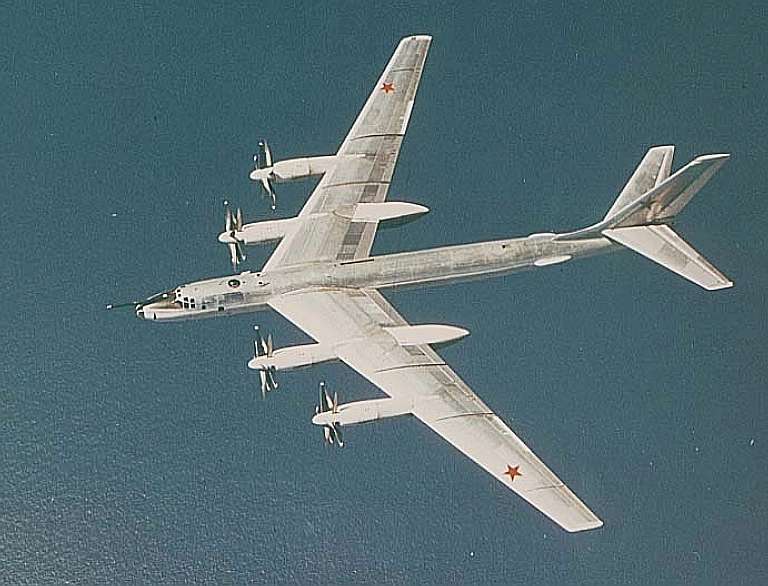  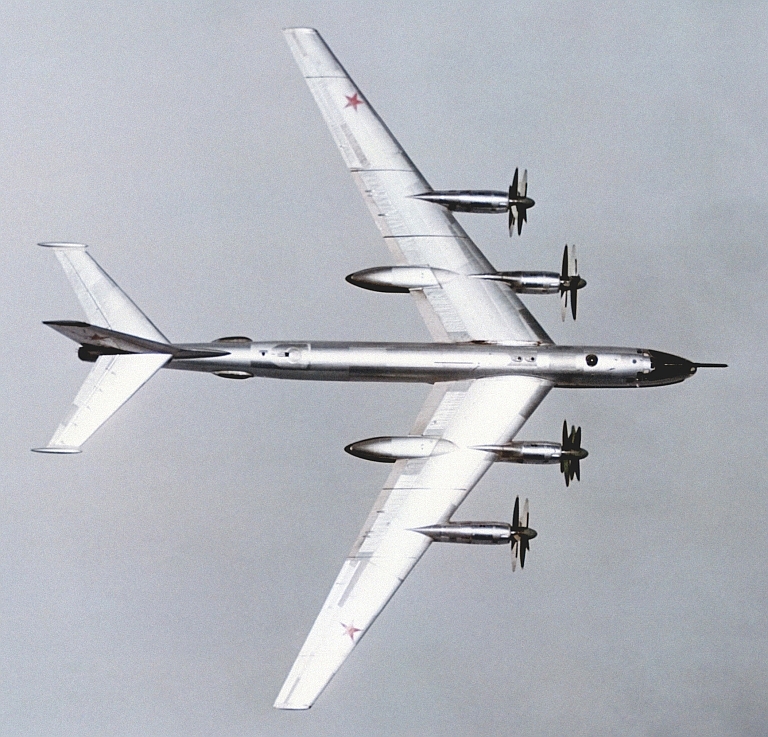  |
|||
Tu-142 Bear F LRMP/ASW Ту-142 Противолодочный самолет  The Tu-142 Bear F is the largest LRMP and ASW aircraft ever built, and one of the highest performing. A number of subtypes exist, and its airframe was the basis for the most recent Bear H strike variant.  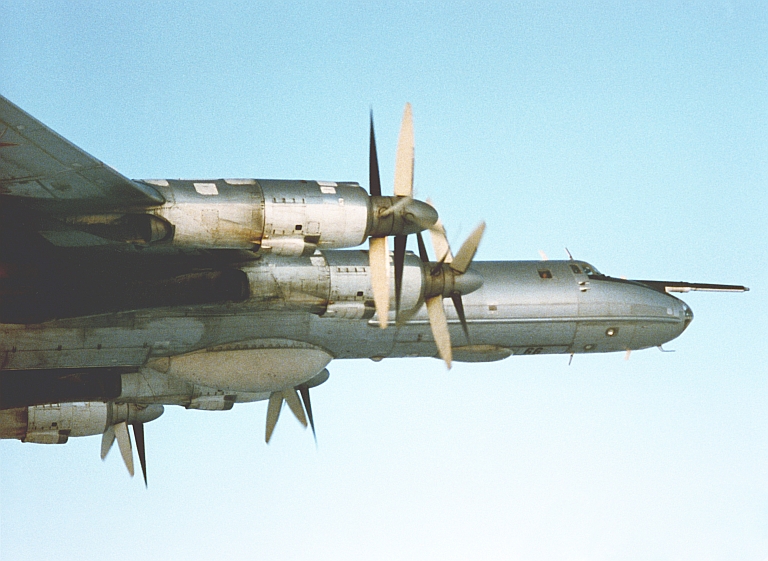   |
|||
Tu-142MR 'Orel' Bear J ELF C3 Relay Ту-142МР 'Орел' Самолет-ретранслятор  The Tu-142MR 'Orel' [Eagle] Bear J is Russia's TACAMO, providing a communications relay capability to submerged SSBNs, SSGNs and SSNs. It is based on the Bear F airframe but has unique systems. The ventral fairing contains the VLF antenna cable reel, also note the unique nose radome and antenna on the vertical tail.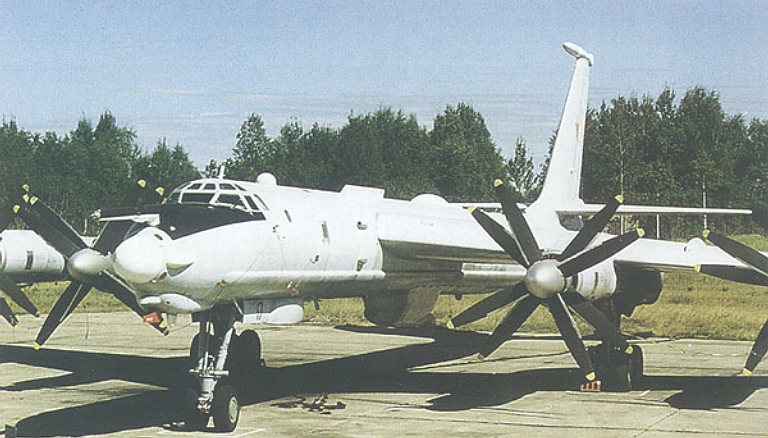  |
|||
| Tu-16K-26/K-10-26 Badger C Maritime Strike Ту-16К-26/К-10-26 Бомбардировщик-ракетоносец  Development of the Tu-16K-10 Badger C started in 1955, the aim being to produce a maritime strike variant capable of carrying the then new Raduga K-10S Luga-S / AS-2 Kipper cruise missile and YeN Puff Ball attack radar designed to support the missile. The starting point was the Tu-16KS Badger B, armed with with the KS-1 Kometa / AS-1 Kennel cruise missile on wing pylon BD-187 launch adaptors, and the Kobalt N fire control system, the weapon system first deployed on the Tu-4 Bull (B-29). The KS-1 was a derivative of the MiG-15 airframe. The new Tu-16K-10 was a major redesign, with the nose resculpted to accommodate the bulbous radome for the YeN, and a revised operator station for the weapon system. The radome geometry was designed to provide significant off-boresight field of regard for the YeN antenna, to permit the Badger to turn away after a missile shot. The K-10S was carried semiconformally on a centreline BD-238 adaptor, and the fuel tank arrangement was modified. A ventral command link antenna was mounted under radome. The design entered service in 1961. A series of progressive block upgrades followed through the life of the design. The K-26 weapon system was retrofitted in 1969, producing the Tu-16K-26, Tu-16K-10-26, and Tu-16K-10-26B Badger C (Mod) variants. The Leninetz Rubin-1KV Short Horn attack radar was retrofitted to support the Raduga KSR-5 / AS-6 Kingfish supersonic ASCM, carried on the BD-487 pylon adaptor. The KSR-5 was a scaled down derivative of the Kh-22 carried by the Tu-22 Blinder and then new Tu-22M Backfire, powered by the smaller S5.33 dual chamber liquid propellant rocket. The Tu-16K-10-26 variant could carry two KSR-5 ASCMs, and one centreline K-10SN Kipper ECM drone. The Tu-16K-26 could carry two KSR-5 ASCMs and one centreline KSR-2 / AS-5A Kelt or KSR-11 / AS-5B Kelt anti-radiation missile. A typical warload was a single KSR-5. The Tu-16K-10-26B subtype was further equipped with bomb racks and the OBP-1RU optical bombsight. Russian sources are not clear on whether the improved 240 NMI range Rubin-1M Short Horn attack radar was later retrofitted to the Badger C. The KSR-11 anti-radiation variant of the Kelt was targeted using the Ritsa homing receiver, which used a nose mounted 8 element interferometer antenna, usually in an inverted T arrangement. It was later replaced with the VSP-K / L-067 Taifun homing receiver in the Tu-16K-10-26P subtype. 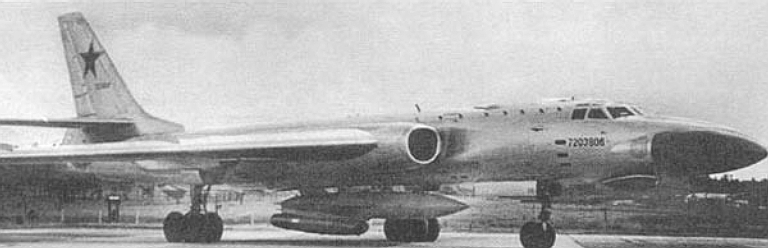 Tu-16K-10 Badger C armed with the Raduga K-10 / AS-2 Kipper cruise missile. 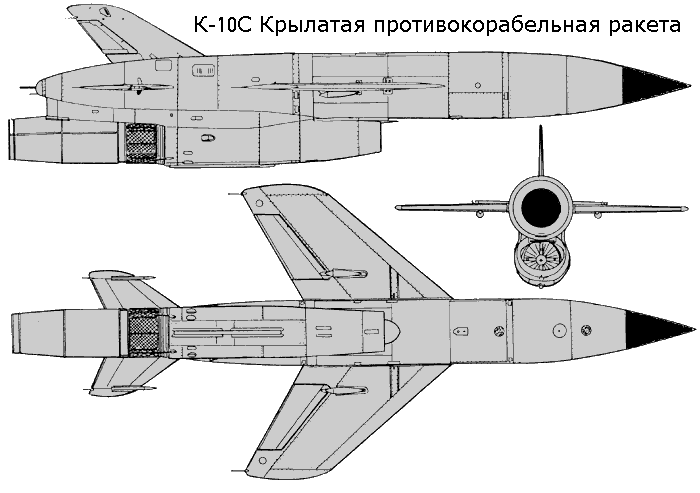 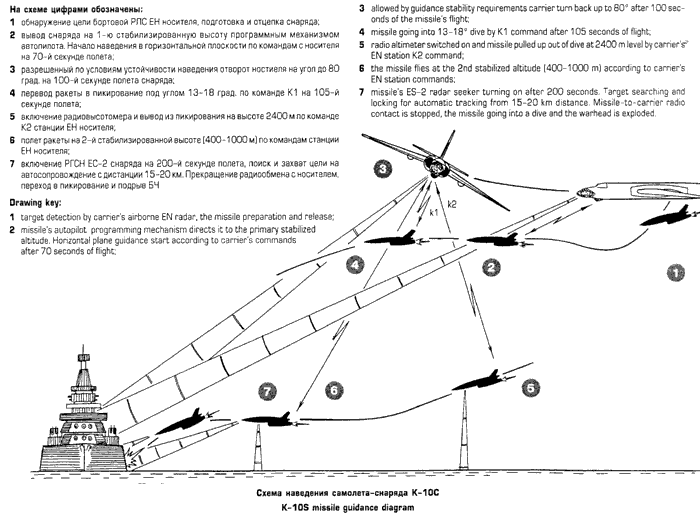  A K-10 Kipper ASCM being loaded on a Badger C (RuMoD).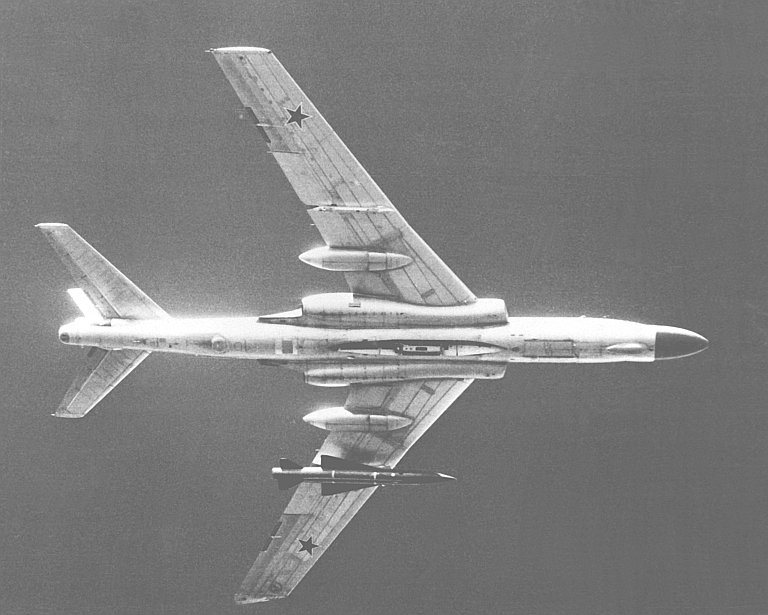  The Tu-16K-26, Tu-16K-10-26, and Tu-16K-10-26B Badger C (Mod) variants were equipped with the new Leninetz Rubin-1KV Short Horn attack radar to support the Raduga KSR-5 / AS-6 Kingfish supersonic ASCM. The missile was based on the large Kh-22 / AS-4 Kitchen.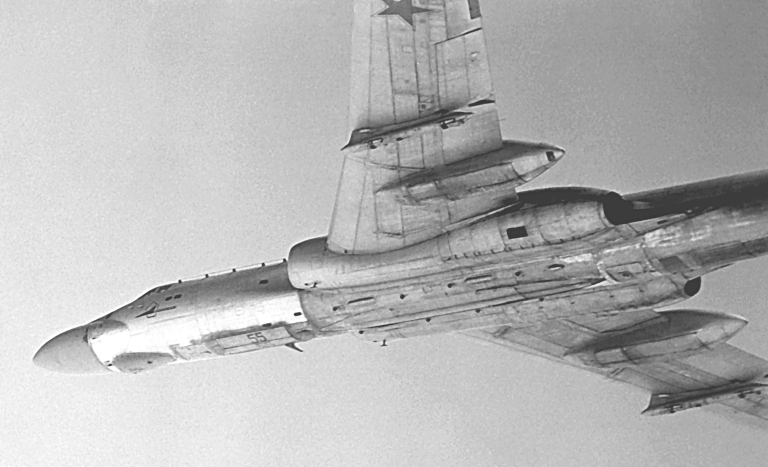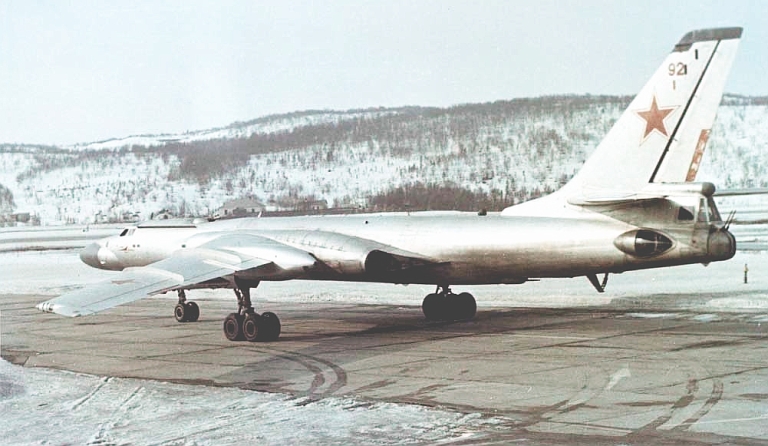       |
|||
| Tu-16RM/RM-1 Badger D Maritime Reconnaissance Ту-16РM/РM-1 Разведчик  The Tu-16RM variant was a dedicated maritime reconnaissance subtype, based on the Badger C. Intended to form the 'Hunter' component of a 'hunter-killer' mix with the Badger C, it is easily distinguished by the absence of missile pylons and the installation of ventral SRS-1M and SRS-4 Romb (Project 30) ESM receiver radomes. These aircraft were equipped with the improved YeN-R Puff Ball, credited with 180 kW peak power and a detection range of 260 NMI. Additional fuel was carried. Around 20 Badger Cs were converted to this configuration.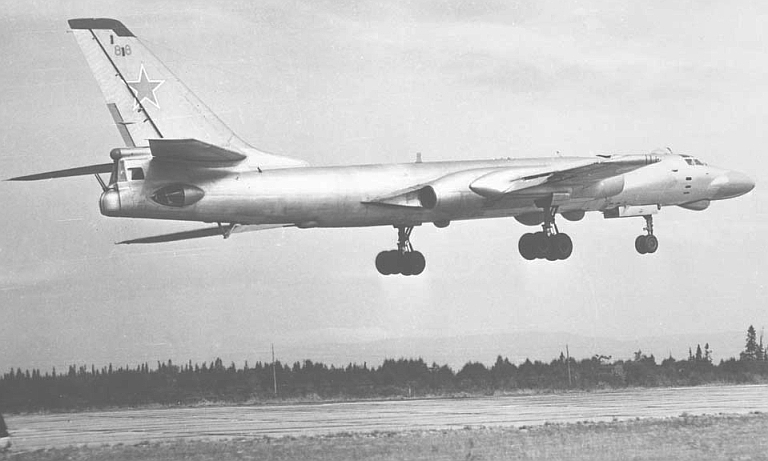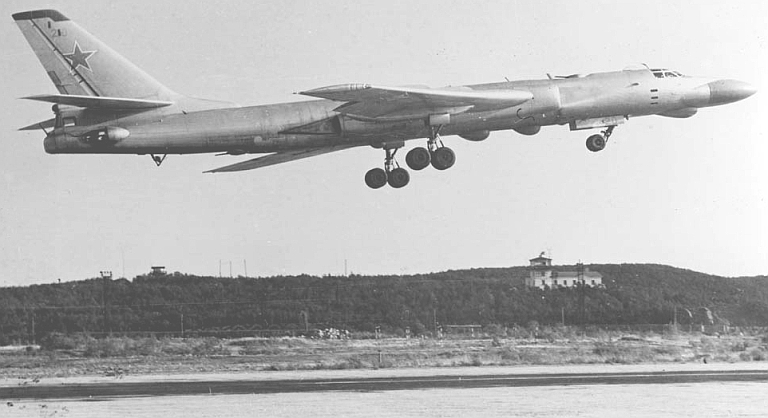   |
|||
Tu-16K-11/K-11-16/K-16-26 Badger G Maritime Strike Ту-16К-11/К-11-16/K-16-26 Бомбардировщик-ракетоносец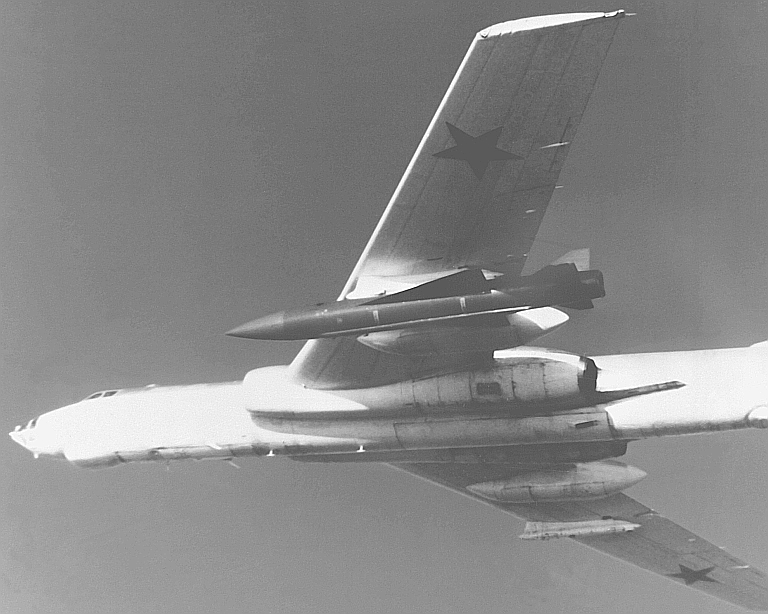  Tu-16K-16-26 Badger G variant equipped with the K-26 weapon system and the KSR-5N / AS-6 Kingfish supersonic ASCM. The Tu-16K-16 Badger G was a block upgrade of the earlier Tu-16KS Badger B, designed to support the KSR-2 / AS-5A Kelt ASCM. Development was initiated almost concurrently with the Badger C, while the KSR-2 was still designated the K-16. The upgrade saw the removal of the KS-1 Kennel weapon system, and retrofit of the new Rubin-1 Short Horn attack radar, DISS-1 Doppler nav, AP-6E autopilot and BD-352 pylon launchers. The Tu-16K-16 Badger G was exported to Egypt and used against Israel. The development of the K-11 weapon system, based on the anti-radiation homing KSR-2P / KSR-11 / AS-5B Kelt ASCM, led to the Tu-16K-11-16 variant, also equipped with the basic Kelt weapon system. To target the anti-radiation variants of the missile, the nose mounted Ritsa homing receiver was fitted (refer Badger C). The third evolution of the Badger G was the Tu-16K-16-26 variant, which introduced the K-26 weapon system and the KSR-5N / AS-6 Kingfish supersonic ASCM, and a comprehensive avionic and systems mid life upgrade. Initially this variant was designated the Ту-16КСР-2-5 / Tu-16KSR-2-5. Most of these aircraft retained the legacy nose radome arrangement, but using an improved Leninetz Rubin-1K Short Horn attack radar, which limited acquisition range to 130 NMI due to antenna size. Badger G aircraft equipped with the Ritsa RHAW acquired during the 1970s the capability to also carry the newer anti-radiation variant of the KSR-5, the KSR-5P. Some Badger Gs were also equipped with the 240 NMI range Rubin-1M attack radar mounted under a bulbous centre-section ventral radome. This solution was required to fit the larger high gain antenna package transplanted from the Berkut surface search radar, otherwise used in the Il-38 May LRMP aircraft. The latter Badger G variant could target shipping at the maximum range of the KSR-5 Kingfish.  Badger G variant equipped with the 240 NMI range increased aperture Rubin-1M attack radar mounted under a bulbous centre-section ventral radome.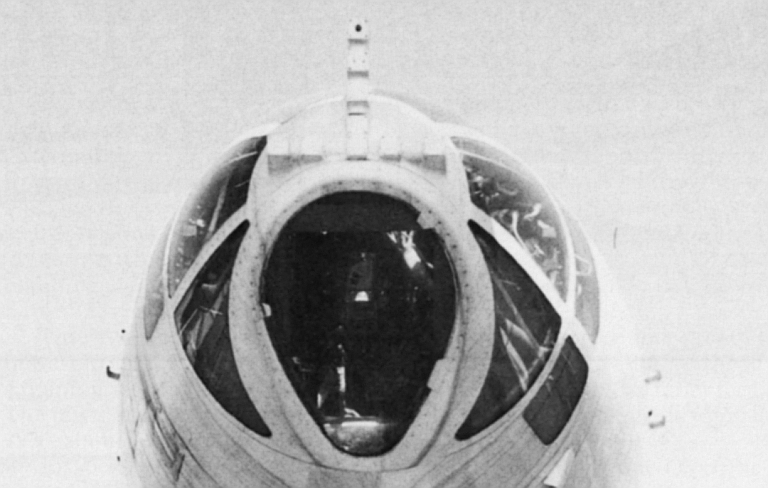   Above: Ritsa RHAW dual-baseline interferometer array used for precision emitter bearing measurements. Below: A pair of AV-MF Tu-16K-11-26P Badger G maritime defence suppression aircraft equipped with the Ritsa RHAW and KSR-5PM anti-radiation missiles. Note the distinctive white AV-MF camouflage paint. This image is unusual as it shows the maximum loadout of two rounds, typically not carried due to range limitations  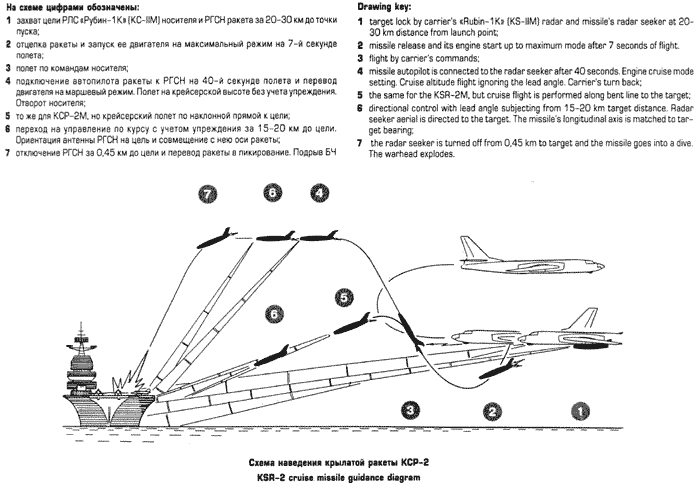 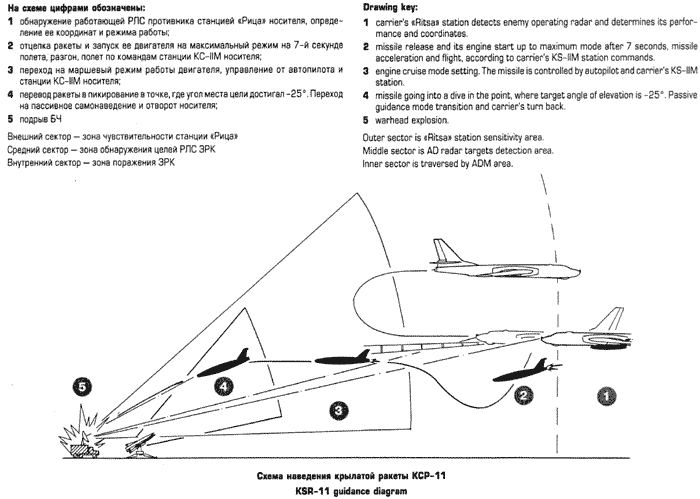 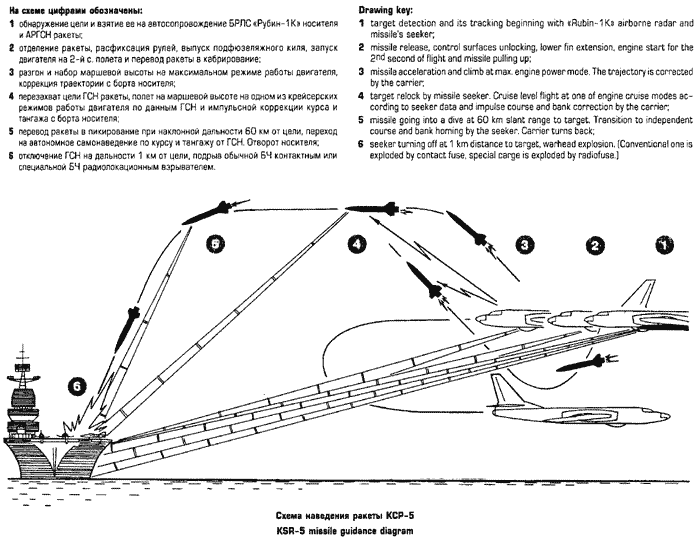  Above, below: Egyptian Tu-16K-16 Badger G were armed with KSR-2 / AS-5 Kelt ASCMs.  |
|||
Tu-16R Badger E/F Tactical Reconnaissance / ELINT Ту-16Р Тактический Разведчик / Cамолет электронной разведки  The Tu-16R Badger E is an ELINT / maritime reconnaissance conversion of the baseline Badger A airframe, equipped with RBP-4 or RBP-6 search radar, and the SRS-1 or SRS-3 ESM receivers. The designation Badger F is usually reserved for the Tu-16R configuration equipped with a podded ESM receiver package. The size and shape of these pods suggests these are related to the podded L-080/081 series Fantasmagoria ESM receivers carried by the Fencer. Some configurations were equipped with optical cameras, and the 75 cm focal length NAFA-MK-75 system for night photography.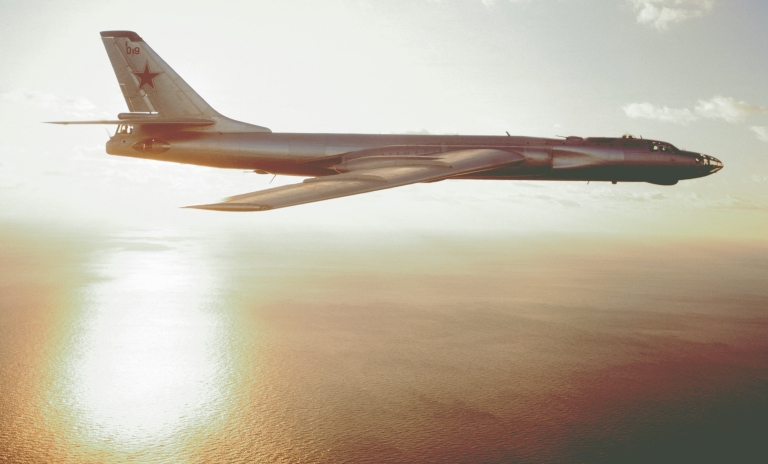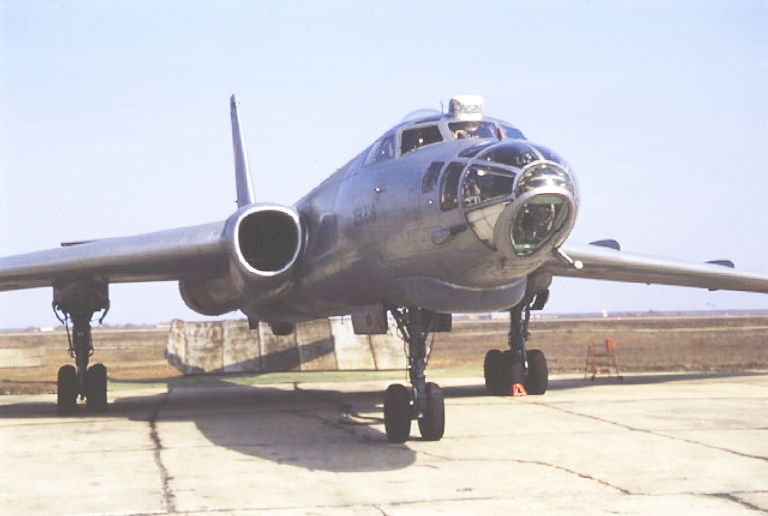    |
|||
Tu-16SPS/Yolka/Ye Badger H/K Electronic Combat Variants Ту-16СПС/Ёлка/E Самолети РЭБ и Электронной разведки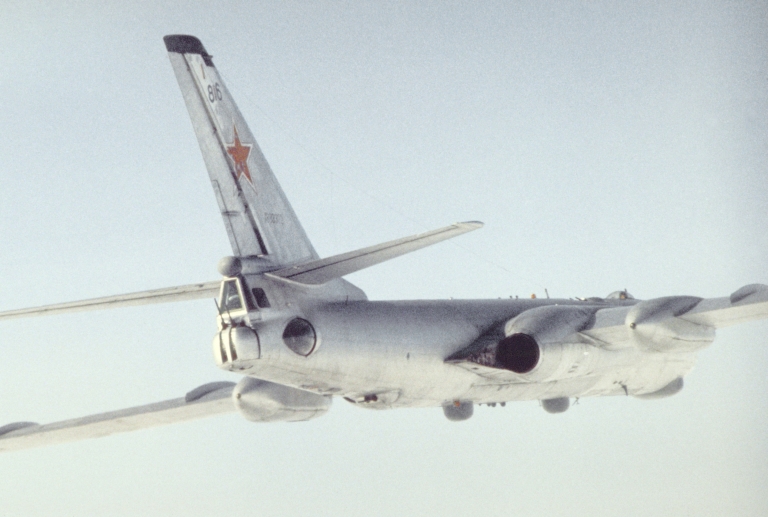  The Soviets deployed a wide range of electronic combat variants of the Badger, and subjected most to various upgrades through their service life. There is little agreement between open sources on the specific configuration of particular subtypes. The Tu-16SPS was the first support jamming variant, equipped with the SRS-1BV and SRS-1D countermeasures receivers, and the SPS-1 low band jammer rated at 120 Watts, and SPS-2 mid band jammer rated at 300 Watts. The Tu-16 Yolka / Badger H was a chaff bomber, with a suite of automatic ASO-16 chaff dispensers in the bomb bay, and an SPS-4M Klyukva jammer later installed.  |
|||
Tu-16P Buket Badger J Electronic Combat Ту-16П Букет Самолет РЭБ и Электронной разведки  The Badger J was the AV-MF equivalent of the EA-6B and EF-111A support jammers, equipped with a bomb bay mounted ventral canoe shaped radome for a suite of steerable jammer emitters. Most were converted from earlier support jamming variants. The tactical jamming system comprised the SPS-22N / SPS-33N / SPS-44N / SPS-55N and SPS-77 Buket, with range of deception and noise jamming modes in several bands. Russian sources claim that in 1972 the Buket was enhanced with the capability to focus its power into a narrow beam, probably by driving multiple emitters coherentlyand using them as a phased array, the upgrade applied to ten aircraft under the designation of "Fikus". During the 1960s some aircraft were also equipped with SPS-100A and SPS-100M high power noise jammers. Some were equipped with the SPS-120 Kaktus jammer, mounted in the bomb bay. Russian sources claim that some of these aircraft were fitted during the 1970s with SPS-151/152/153 Lyutik self protection jammers, common to the MiG-25RBV and MiG-25BM Foxbat, and the Tu-95K-22 Bear G. This equipment used the same antenna arrangement and tailcone fairing as the Azaliya equipped Badger L. As with the Badger L, there is considerable disagreement between open sources on the equipment fit in the Badger J series of EW subtypes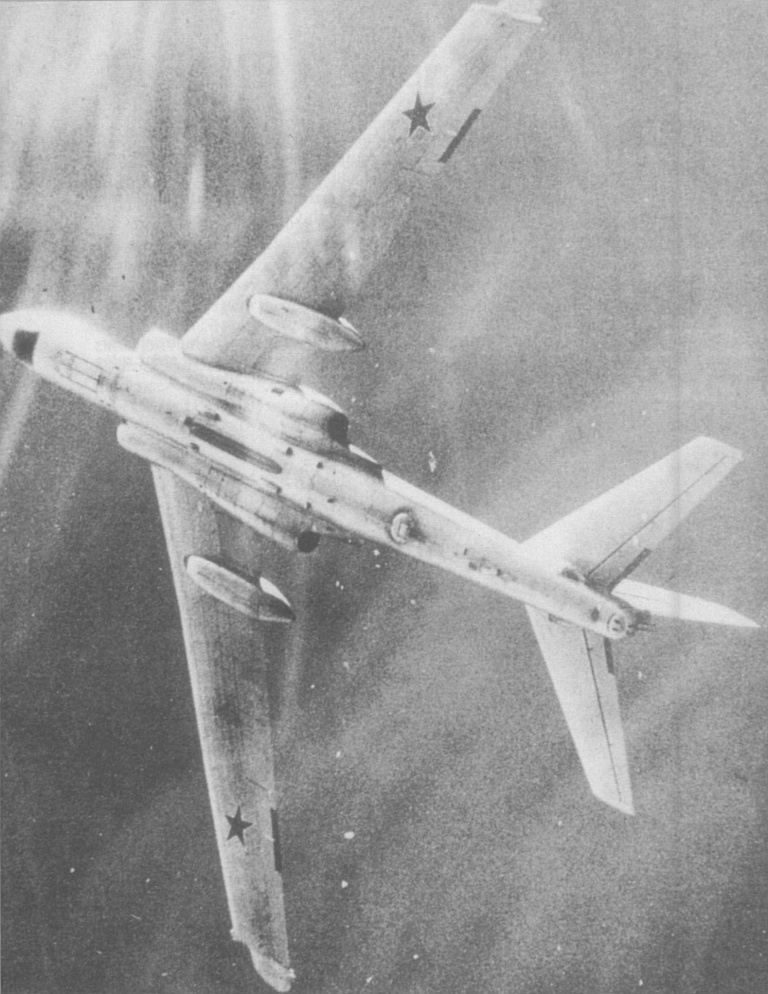  |
|||
Tu-16Ye/YeR/P/PN/PP Azaliya Badger L Electronic Combat Ту-16E/EР/П/ПH/ПП Азалия Самолети РЭБ и Электронной разведки 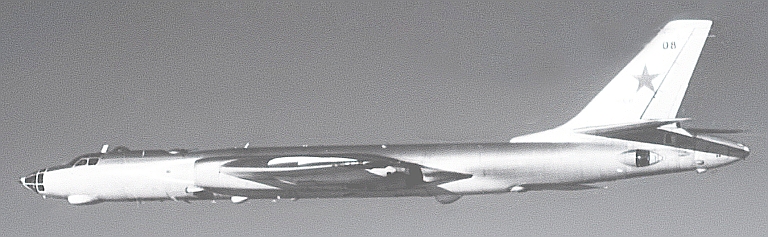 Several configurations of the Tu-16Ye have been reported, equipped with SPS-6 Los and SPS-61, SPS-62, SPS-63 Azaliya jammers. Another configuration used the SPS-5 Fasol noise jammer and SPS-64, SPS-65, SPS-66 Azaliya jammers. Some aircraft were also equipped with SPS-100A and SPS-100M high power noise jammers. Russian sources claim that many of these aircraft were equipped during the 1970s with SPS-151/152/153 Lyutik self protection jammers, common to the MiG-25RBV, MiG-25BM Foxbat and Tu-95K-22 Bear G. This equipment used emitters in the nose thimble radome, the antennas below the inlets, and the unique tailcone fairing which replaced the 23 mm gun equipped DK-7 tail turret. Some aircraft have been photographed with chaff dispensing pods, other podded ESM receivers identical to the type carried by the Badger F. The Tu-16YeR was an electronic reconnaissance adaptation using the SRS-1 ELINT receiver instead of the SPS-2 installation. The SPS-61R, SPS-63R Azaliya X-band jammers are also reported as equipment in the K-10SP powered ECM drone, launched by the Tu-16K-10 Badger C. There is considerable disagreement between open sources on the equipment fit in the Badger L series of EW subtypes - the aircraft is often credited with carrying components of the Buket suite. The ventral blister radomes are characteristic of the mid and high band components of the SRS-1 and SRS-4 ESM receivers used in various reconnaissance subtypes. 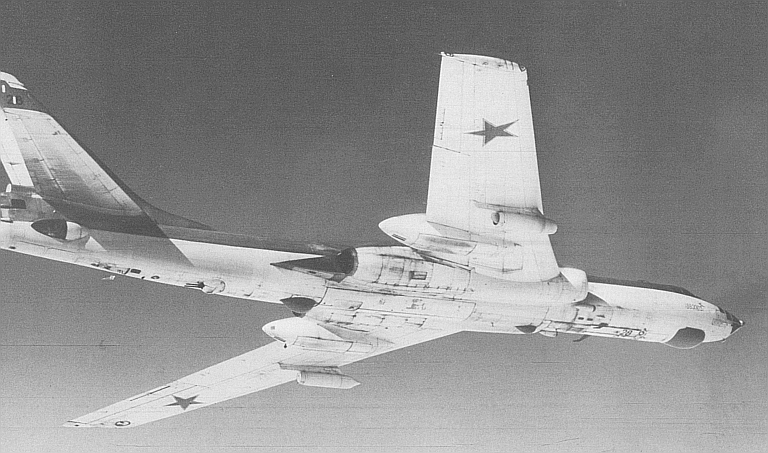    |
|||
Tu-22M2 Backfire B Ту-22M2 Бомбардировщик-ракетоносец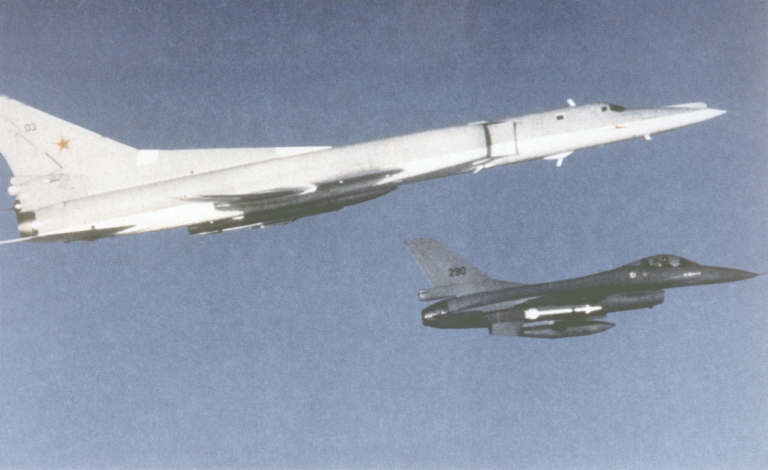  The underpowered Tu-22M2 Backfire B was the first production model, or which over 200 were built (US DoD).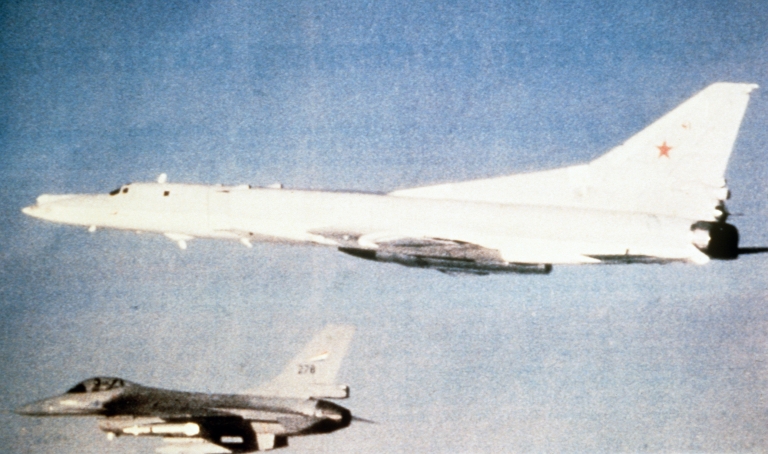   |
|||
Tu-22M3 Backfire C Ту-22M3 Бомбардировщик-ракетоносец Technical Report APA-TR-2007-0701 Tupolev Tu-22M3 Backfire C Bomber - missile carrier [Click for more ...]     The centreline Kh-22 store is carried semi-conformally, with sculpted bomb bay doors to accommodate the weapon. The bomb bay rotary launcher is otherwise used for a range of weapons (US DoD).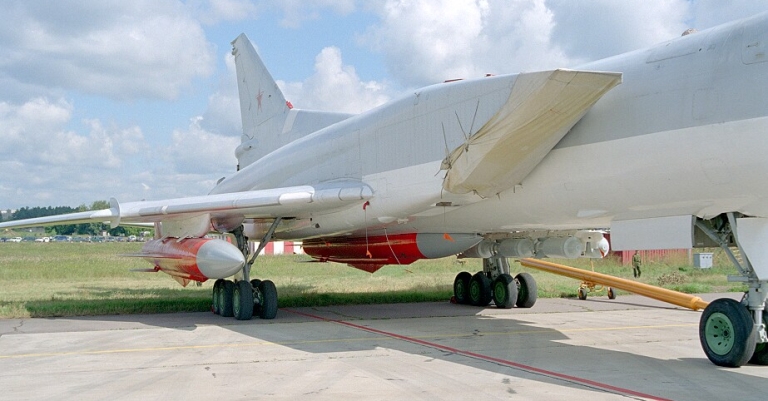  Outboard glove station BD-45K adaptors are used to carry a pair of external Kh-22 rounds, but can be replaced with bomb racks for up to 3 tonnes of free fall bombs. (via Wikipedia).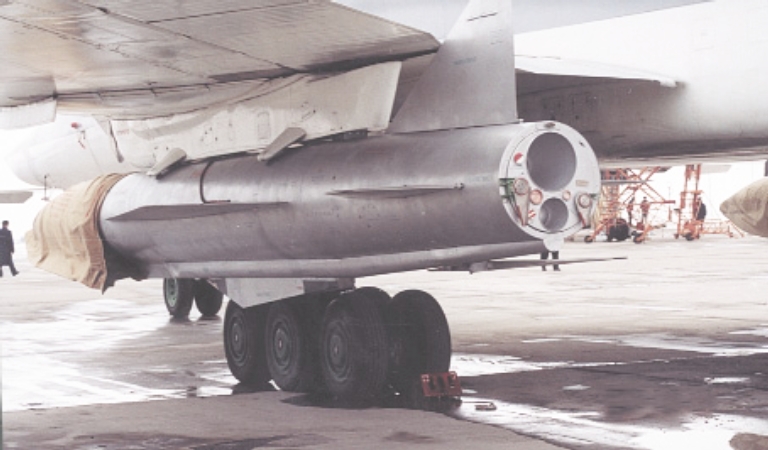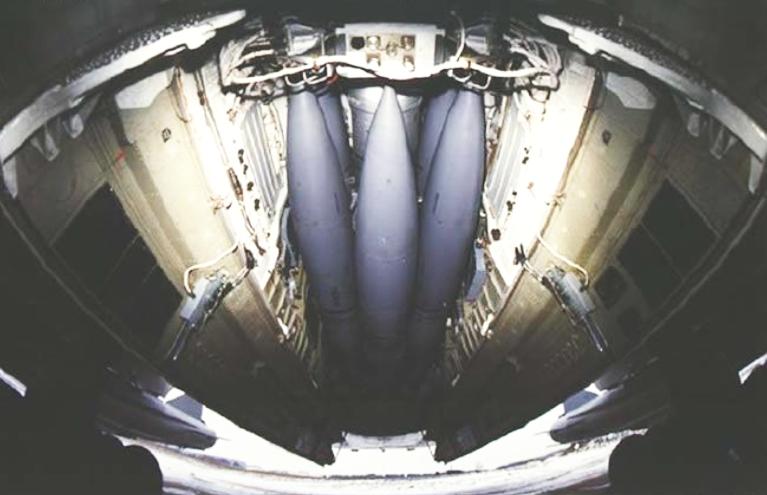   The Kh-15 / AS-16 Kickback is the Russian equivalent to SAC's AGM-69 SRAM. Note the maritime strike CONOPS uses offboard targeting provided by the Tu-95RTs Bear D Uspekh / Big Bulge X-band surveillance and targeting radar (via Warfare.ru).
|
إعـــــــلان
تقليص
لا يوجد إعلان حتى الآن.
Soviet Maritime Reconnaissance
تقليص
X
-
Soviet Maritime Reconnaissance
سحابة الكلمات الدلالية
تقليص
ما الذي يحدث
تقليص
المتواجدون الآن 0. الأعضاء 0 والزوار 0.
أكبر تواجد بالمنتدى كان 182,482, 05-21-2024 الساعة 06:44.




تعليق